
MP.8 - Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning.
MP.7 - Look for and make use of structure.MP.5 - Use appropriate tools strategically.MP.3 - Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
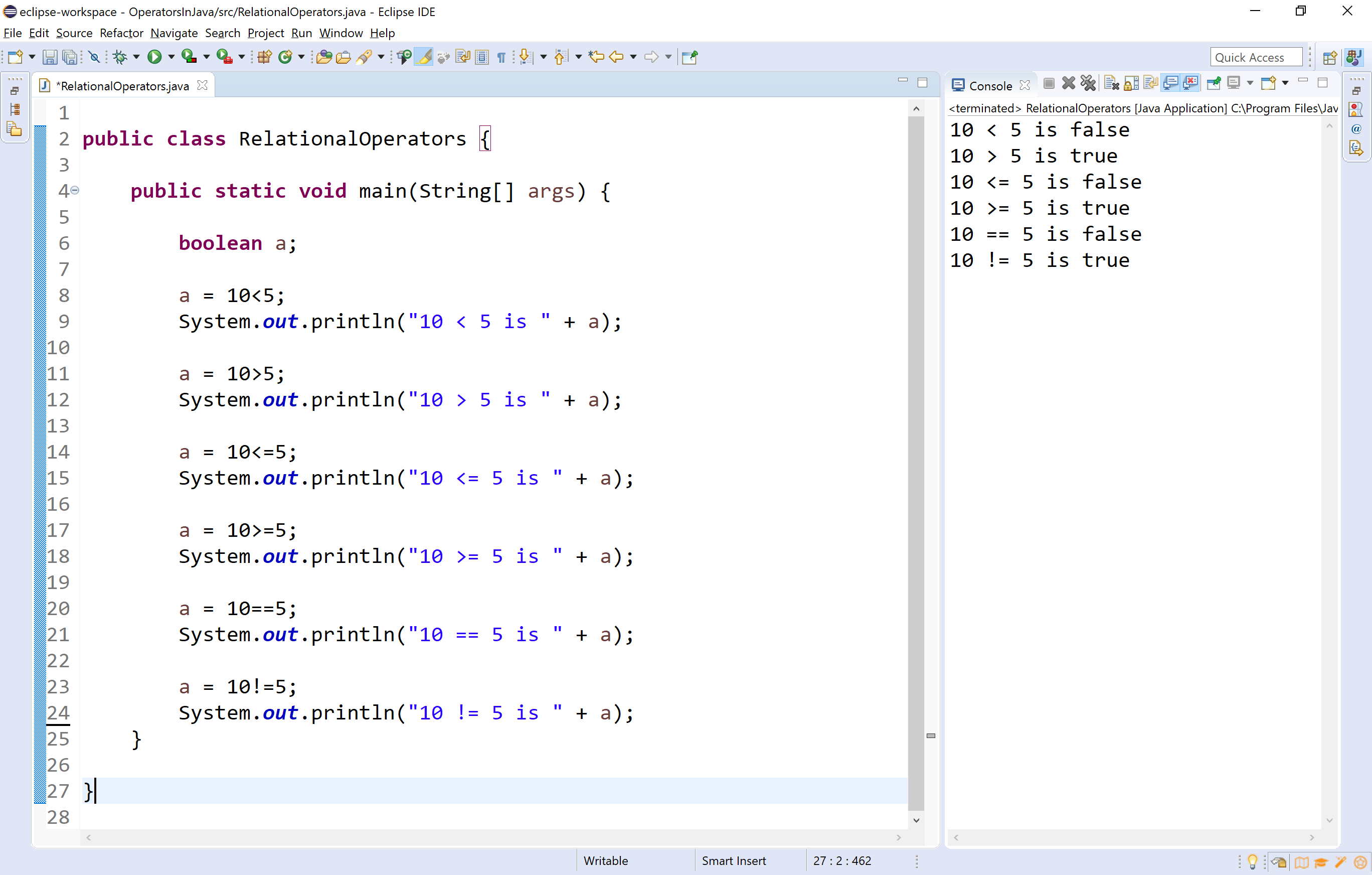
 MP.1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. For example, given a linear function represented by a table of values and a linear function represented by an algebraic expression, determine which function has the greater rate of change. 8.F.2 - Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output.1 8.F.1 - Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. 7.EE.4 - Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. For example, in a problem involving motion at constant speed, list and graph ordered pairs of distances and times, and write the equation d = 65t to represent the relationship between distance and time. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. 6.EE.9 - Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.NS.8 - Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). 5.OA.2 - Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. 5.OA.1 - Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. Therefore, when Boolean operators are used in the same expression as Relational operators, the Boolean operators will be executed first. Standards Alignment Common Core Math Standards Boolean (, &,, ) operators have a higher precedence level than Relational ( <, <, >, >,, ) operators.
MP.1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. For example, given a linear function represented by a table of values and a linear function represented by an algebraic expression, determine which function has the greater rate of change. 8.F.2 - Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output.1 8.F.1 - Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. 7.EE.4 - Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. For example, in a problem involving motion at constant speed, list and graph ordered pairs of distances and times, and write the equation d = 65t to represent the relationship between distance and time. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. 6.EE.9 - Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.NS.8 - Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). 5.OA.2 - Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. 5.OA.1 - Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. Therefore, when Boolean operators are used in the same expression as Relational operators, the Boolean operators will be executed first. Standards Alignment Common Core Math Standards Boolean (, &,, ) operators have a higher precedence level than Relational ( <, <, >, >,, ) operators.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
